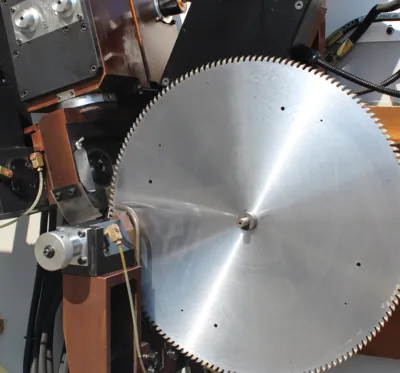
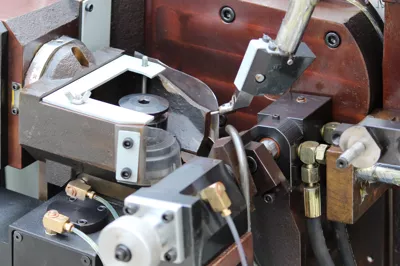
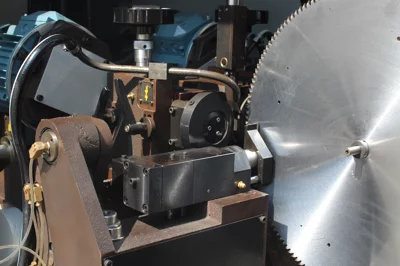
The main points of choosing carbide circular saw blades
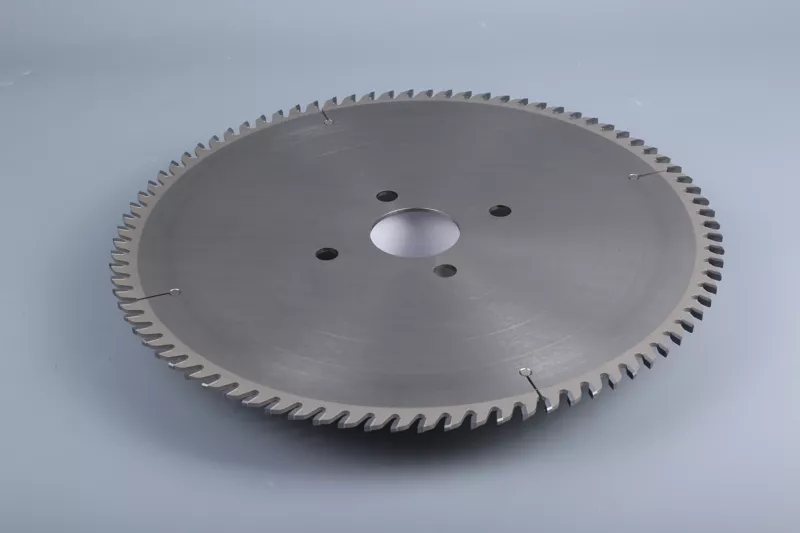

The parameters of hard alloy circular saw blades include alloy blade type, matrix material, diameter, number of teeth, thickness, tooth shape, angle, and aperture, which determine the cutting ability and cutting performance of the saw blade. When selecting a saw blade, the appropriate one should be chosen based on the type, thickness, speed, and direction of the material to be cut, as well as the feed speed and saw kerf width.
1. Selection of diameter
The diameter is related to the equipment used and the thickness of the workpiece. A smaller diameter corresponds to a lower cutting speed, while a larger diameter requires higher speed and higher efficiency. Different models can use standard parts with corresponding diameters or 120mm precision slotted saw blades.
Standard diameters include: 110mm (4 inches), 150mm (6 inches), 180mm (7 inches), 200mm (8 inches), 230mm (9 inches), 250mm (10 inches), 300mm (12 inches), 350mm (14 inches), 400mm (16 inches), 450mm (18 inches), 500mm (20 inches), etc. Precision slotted saw blades for precision cutting boards are mostly designed with a width of 120mm.
2. Selection of number of teeth
The number of teeth on the saw blade determines the number of cutting edges in a unit of time and the cutting performance. Generally, the more teeth, the better the cutting performance. However, using more hard alloy for a higher number of teeth will result in a higher cost. Additionally, a high density of teeth reduces the amount of chip space between teeth, which can lead to saw blade overheating. Furthermore, too many teeth will result in minimal cutting volume per tooth if the feed rate is not properly matched, which can increase friction between the cutting edge and the workpiece, affecting the service life of the blade. Normally, the tooth pitch is between 15-25mm, and the number of teeth should be chosen based on the material to be cut.
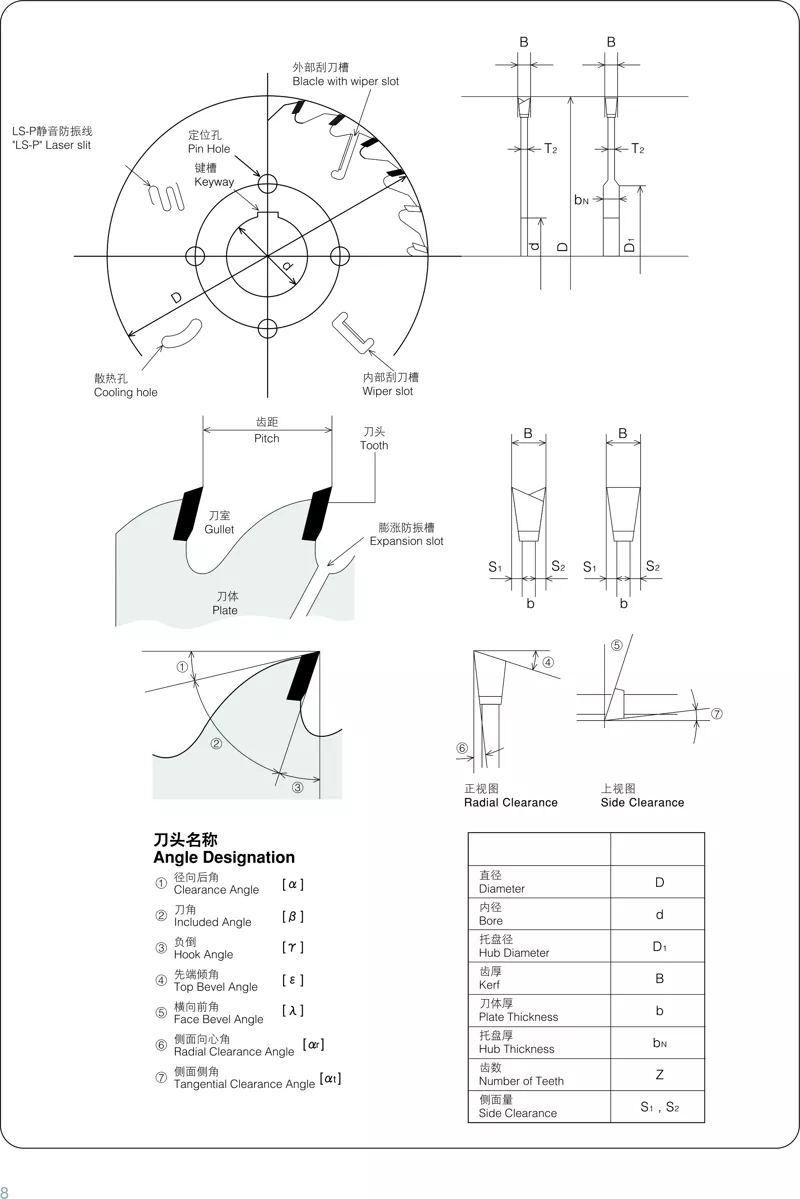
3. Selection of thickness.
In theory, a thinner blade is preferred, but in actual practice, a blade that is too thin can cause instability and affect the cutting performance. Therefore, thickness should be selected considering stability and material characteristics. Certain special requirements may require the use of specific thicknesses according to equipment requirements, such as for slitting or marking.
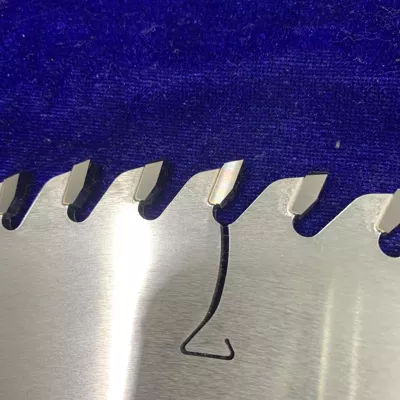
4.Selection of tooth shape
Common tooth shapes include alternating teeth, flat teeth, ladder teeth (high and low teeth), inverted ladder teeth (reverse cone teeth), dovetail teeth (camel teeth), as well as less common industrial-grade tooth shapes like three left one right and alternating flat teeth.
4.1. Alternating teeth are the most widely used tooth shape, providing fast cutting speed and relative ease of sharpening.
They are suitable for cutting various soft and hard solid wood profiles, as well as density boards, plywood, particle boards, etc. The alternating teeth with anti-kickback teeth are called dovetail teeth, which are suitable for longitudinal cutting of boards with knots. Saw blades with negative rake angle have sharp teeth and excellent cutting quality, and are usually used for cutting veneer boards.
4.2. Flat teeth provide a rougher cut, slower cutting speed, and easiest sharpening.
They are mainly used for cutting ordinary wood, and are cost-effective. They are often used for small diameter aluminum saw blades to reduce adhesion during cutting, or for slotting saw blades to maintain a smooth bottom of the slot.
4.3. Ladder teeth are a combination of ladder teeth and flat teeth, and require more complex sharpening.
They can reduce chipping during cutting, making them suitable for cutting various single or double-sided veneer boards and fireproof boards. For aluminum saw blades, ladder teeth with a higher number of teeth are often used to prevent adhesion.
4.4. Inverted ladder teeth are commonly used in slotted saw blades. When cutting double-sided veneer boards, the slot saw is adjusted to a certain thickness to complete the groove processing on the bottom surface, and then the main saw is used to cut the board to prevent chipping at the cutting edge.

DM100 face and top grinding machine
5.Examples of tooth shape can be seen in the provided images.
In conclusion, for cutting solid wood, particle boards, and medium-density boards, alternating teeth should be chosen to cleanly cut through the wood fiber tissue and provide a smooth cut. For slotting to maintain a smooth bottom, flat teeth or a combination of alternating and flat teeth can be used. For cutting veneer boards and fireproof boards, ladder teeth are generally selected. CNC saws, due to their high cutting rate, use larger diameter and thickness hard alloy saw blades, usually with a diameter of around 350-450mm and a thickness between 4.0-4.8mm. Most of these saw blades use ladder teeth to reduce chipping and saw marks.
With years of hands-on experience, I have honed my skills in navigating the complexities of global commerce, offering invaluable insights and solutions to address customer needs. My commitment to excellence and dedication to customer satisfaction ensure that I deliver exceptional service, guiding clients through every step of the trading process with confidence and proficiency.